※Canteraバージョン:3.1.0
Canteraでプラグフロー反応器をモデル化するにはいくつかの異なる手法がある。
目次
ゼロ次元反応器の連結
一つ目は、ゼロ次元の反応器を連続して接続し、上流側から順に解いていく方法。これは、以下の記事で詳しく紹介している。
ラグランジェ的手法
二つ目は、Canteraのサイトでラグランジェ的な手法(Lagrangian Particle Simulation)として紹介されている方法。
https://cantera.org/stable/examples/python/reactors/pfr.html
IdealGasConstPressureReactorを使って時間発展を計算している。一つ目の例と同じ問題で解くとすると、以下のようになる。
import cantera as ct
import csv
# Simulation parameters
p = ct.one_atm # pressure [Pa]
Tin = 1500.0 # inlet temperature [K]
comp = 'CH4:1, O2:1, AR:0.5'
vin = 0.005 # inlet velocity [m/s]
length = 5e-6 # reactor length [m]
area = 1e-4 # cross section area [m2]
n_step = 1000 # number of divided reactor
# define object
gas = ct.Solution('gri30.yaml')
gas.TPX = Tin, p, comp
mdot = vin * area * gas.density
r = ct.IdealGasConstPressureReactor(gas)
sim = ct.ReactorNet([r])
t_total = length / vin
dt = t_total / n_step
# solve
outfile = open('pfr.csv','w', newline='')
writer = csv.writer(outfile)
writer.writerow(['distance', 'velocity', 'rtime', 'T', 'P'] + gas.species_names)
rtime = 0.0
dist = 0.0
for n in range(n_step):
rtime += dt
sim.advance(rtime)
u = mdot / area / r.thermo.density # velocity
dist += dt * u
writer.writerow([dist, u, rtime, r.T, r.thermo.P] + list(r.thermo.X))
if dist >= length:
break
outfile.close()FlowReactorを使う
三つ目は、FlowReactor反応器オブジェクトを使う方法。
https://cantera.org/stable/examples/python/reactors/surf_pfr.html
次のようなコードで計算できる。
import cantera as ct
import csv
# Simulation parameters
p = ct.one_atm # pressure [Pa]
Tin = 1500.0 # inlet temperature [K]
comp = 'CH4:1, O2:1, AR:0.5'
vin = 0.005 # inlet velocity [m/s]
length = 5e-6 # reactor length [m]
area = 1e-4 # cross section area [m2]
# define object
gas = ct.Solution('gri30.yaml')
gas.TPX = Tin, p, comp
mdot = vin * area * gas.density
r = ct.FlowReactor(gas)
r.mass_flow_rate = mdot / area
sim = ct.ReactorNet([r])
# solve
outfile = open('pfr_2.csv','w', newline='')
writer = csv.writer(outfile)
writer.writerow(['distance', 'velocity', 'rtime', 'T', 'P'] + gas.species_names)
while sim.distance < length:
dist = sim.distance
rtime = sim.step()
writer.writerow([dist, r.speed, rtime, r.T, r.thermo.P] + list(r.thermo.X))
print(rtime, dist)
outfile.close()FlowRactor反応器を定義して、内部で時間発展の計算を行う。
結果の比較
それぞれの手法で計算結果を比較してみる。まず、濃度の分布を示す。
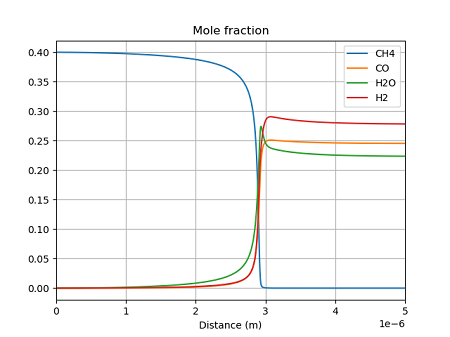
ゼロ次元反応器
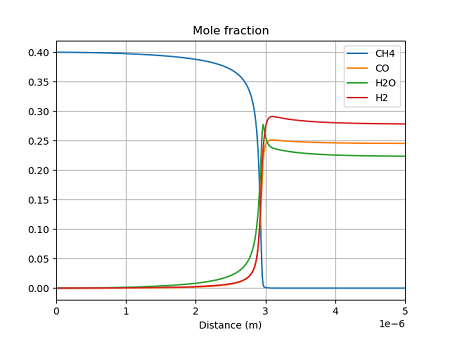
ラグランジェ手法
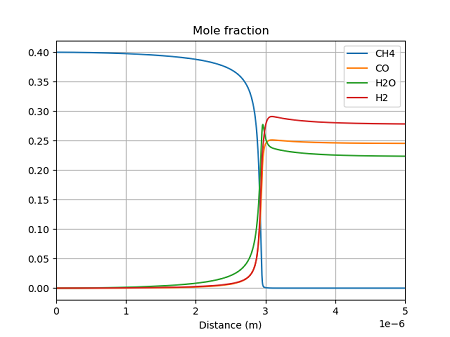
FlowReactor
次に温度分布を示す。
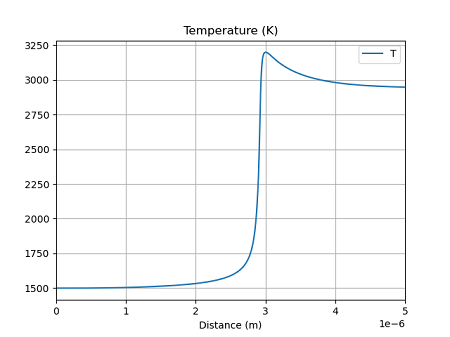 ゼロ次元反応器
ゼロ次元反応器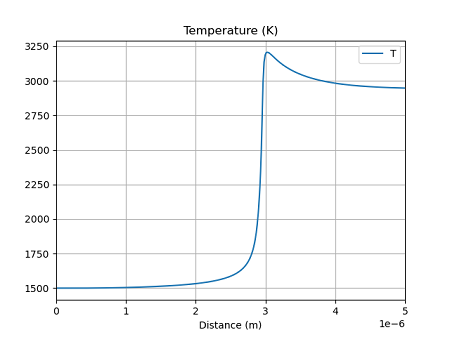
ラグランジェ手法
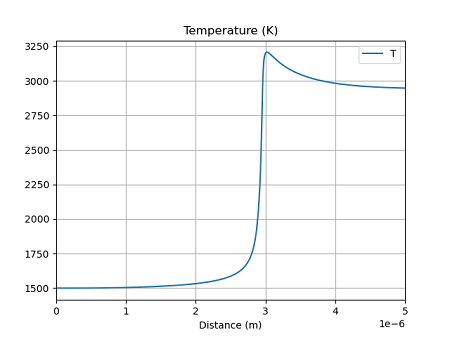
FlowReactor
どの手法でも、ほぼ同じ結果となっている。
ラグランジェ手法やFlowReactorはコードを簡潔に書ける。また、ゼロ次元反応器の連結手法は、対向流熱交換器などで他のプラグフロー反応器と熱連成を行ったり自由度のあるモデリングができる。場合により使い分けるとよいだろう。
