※Canteraバージョン:3.1.0
Canteraは、Pythonの他にもC++やFORTRANなどの言語でも使用することができる。
目次
ソースコードのコンパイル
CanteraはC++でソースコードが書かれているため、自分のC++プログラムにCanteraのライブラリをリンクして使用することができる。
そのためには、以下の公式サイトの方法で、ライブラリをインストールして使うか、
https://cantera.org/stable/install/conda.html#sec-conda-development-interface
もしくは、以下のページのようにCanteraのソースコードをダウンロードして、ソースからコンパイルする。
https://cantera.org/stable/develop/index.html#sec-compiling
コンパイラは、GNU、Microsoft Visual Studio、Intel compiler、MinGWなどに対応しているので、自分の環境にあったもので構築できる。
今回は、WindowsのAnaconda環境にライブラリをインストールしCMake(MSVC)でビルドした。なお、MinGW-W64でソースからコンパイルしたライブラリを使っても同じ結果であった。
着火遅れ時間の計算
以下のPythonで行った着火遅れ時間の計算をC++で書いて計算してみる。
C++プログラム
全体のフローは、基本的に上記のPythonプログラムと対応している。
CanteraのC++ドキュメントは以下を参照。
https://cantera.org/stable/cxx/index.html
今回のプログラムのソースコード(GitHub)
#include "cantera/core.h"
#include "cantera/zerodim.h"
#include "cantera/kinetics.h"
#include "cantera/base/Array.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace Cantera;ヘッダーとCanteraのnamespaceを設定。
// define gas state
auto sol = newSolution("LLNL_heptane_160.yaml");
auto gas = sol->thermo();
gas->setState_TP(temp, p);
gas->setEquivalenceRatio(phi, "nc7h16", "o2:1.0, n2:3.76");newSolutionで反応メカニズムファイルを指定。ここでは、gasに状態量をセットする。
// define reactor
IdealGasReactor r;
r.setSolution(sol);
ReactorNet sim;
sim.addReactor(r);IdealGasReactorの反応器オブジェクトと反応器ネットワークを定義する。
// time loop
double time = 0.0;
int nstep = tend / dt;
Array2D states(2, nstep);
for (int i = 0; i < nstep; i++)
{
sim.advance(time);
states(0, i) = time;
states(1, i) = r.contents().temperature();
time += dt;
}時間発展して反応計算を行う。Array2Dは、2次元配列のクラスで、時間と温度を格納するのに使っている。
// ignition delay time
double diffMax = 0.0;
int ix = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nstep - 1; i++)
{
double diff = states(1, i + 1) - states(1, i);
if (diff > diffMax)
{
diffMax = diff;
ix = i;
}
}
double time_igd = states(0, ix);
std::cout << "Ignition Delay Time: " << time_igd * 1e6 << " micro sec" << std::endl;ここでは、温度勾配が最大となる時刻を取得し、着火遅れ時間time_igdとしている。
// write csv
std::ofstream file("output.csv");
file << "time,temperature" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < nstep; i++)
{
file << states(0, i) << "," << states(1, i) << std::endl;
}
file.close();Pythonではグラフ出力しているが、ここではCSVファイルに結果を出力している。
結果
結果はPythonと同じである。
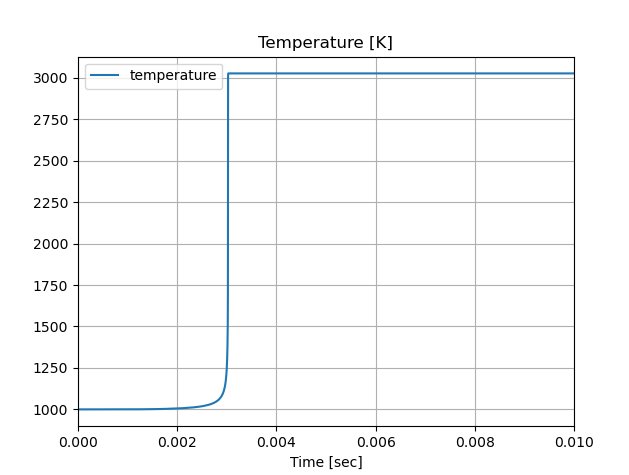
自分のプログラムに化学反応計算を組み込みたい場合など色々使える。
